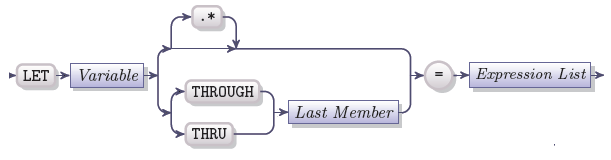
LET
LET statement is used to assign a value or a set of values to a variable or a record.
|
Variable |
A variable which is assigned a value |
|
Expression list |
One or more 4GL expressions that return the value which is assigned to the variable |
|
Last member |
The last record member of the specified set of members (if the "variable" represents the first member of the sequence) |
A variable of any data type except for the object data types (e.g. WINDOW, FORM) can be assigned values with the help of the LET statement.
When a variable is declared with the help of the DEFINE statement, it has no value, but the memory space is allocated to it. There are two ways of initializing a variable (that is of assigning some value to it): the use of the INITIALIZE statement or the LET statement. Do not use a variable that has not been initialized in a 4GL expression, the value returned by such expression will hardly prove to be useful.
When 4GL encounters a LET statement, it evaluates the expression to the right of the equal sign (=) and then assigns it to the variable. The following example illustrates assignment of values to variables:
DEFINE a, b, c, d INT
LET a = 2
LET b = 5
LET c = a + b
LET d = NULL
Most of the 4GL built-in functions and operators can be used in the LET statement. The example below assigns an ASCII symbol to the variable. The displayed value will be "d":
DEFINE var1 CHAR(1)
LET var1 = ASCII 100
DISPLAY var1
You cannot assign individual values to a program record with the help of the LET statement, you cannot use the THRU/THROUGH keyword as well. However, you can assign values of one program record to another program record with the help of the .* notation, provided that the both records have the same number of members and the members are of compatible data types:
LET rec1.* = rec2.*
LET statement can be used to assign a value to a sub-string of CHAR, STRING or VARCHAR data type:
DEFINE full_name CHAR (30), fname CHAR (15)
LET full_name[1,15] = fname
The LET statement can assign only NULL values to the variables of the Large data types. To assign other values to such variables use the INTO clause in a SELECT, FOREACH, OPEN, or FETCH statement or pass the name of such variable as an argument to a function.