Querix 4gl provides some useful algorithms which greatly enhance search with regular expressions.
Tests STRICTLY the occurrence of a regular expression within a given string. The whole string must match the whole regular expression and vice versa.
Syntax:
util.regex.match(s STRING, re REGEX)
Parameters:
|
re |
input string |
|
s |
regular expression that will be matched against the input string |
Returned values:
Returns true if a match exists. Otherwise, returns false.
Usage and examples:
DEFINE regex util.REGEX
DEFINE rs STRING
DEFINE r BOOL
...
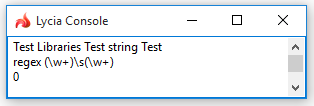
LET regex = /(\w+)\s(\w+)/
LET r = util.REGEX.match(rs, regex)
DISPLAY r
Searches when a regular expression occurs within a given string. The expression can be only a part of the searched string.
Syntax:
util.regex.search(s STRING, re REGEX) RETURNING match MATCH_RESULTS
Parameters:
|
re |
input string |
|
s |
regular expression that will be searched for in the input string |
Returned values:
|
m |
returns the search results must be a MATCH_RESULTS object |
|
m.prefix() |
returns the string that precedes the matched string |
|
m.suffix() |
returns the string that follows the matched string |
|
m.size() |
returns the number of the marked sub-expressions plus 1 |
|
m.str(0) |
returns string that matches the regular expression |
|
m.length(0) |
returns the length of the matched regular expression |
|
m.position(0) |
returns the position of the matched regular expression starting from the beginning of the string |
|
m.matched(0) |
returns true if a full match was found, and false if it was a partial match |
|
m.str(n) |
returns the string that matched the sub-expression n |
|
m.length(n) |
returns the length of the sub-expression n |
|
m.position(n) |
returns the position of the sub-expression n starting from the beginning of the string |
|
m.matched(n) |
returns true if the sub-expression n was in the match; otherwise, returns false |
Usage and examples:
DEFINE regex util.REGEX
DEFINE m util.MATCH_RESULTS
DEFINE rs STRING
DEFINE r BOOL
...
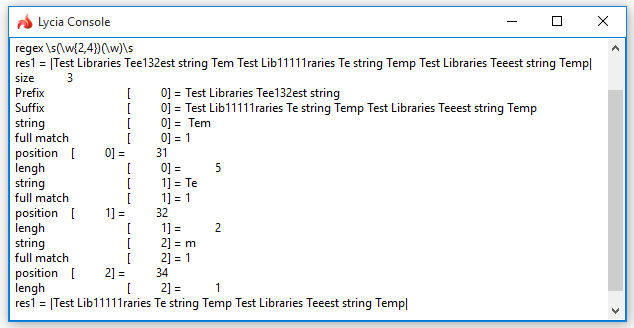
LET regex = /(\w+)\s(\w+)/
CALL util.REGEX.search(rs, regex) RETURNING m
...
DISPLAY m.size()
DISPLAY m.prefix()
DISPLAY m.suffix()
...
Replaces a string matching one regular expression with a string matching the other regular expression.
Syntax:
util.regex.search(s STRING, re REGEX, fmt STRING) RETURNING rpl STRING
Parameters:
|
re |
input string |
|
s |
regular expression that will be matched against the input string |
|
fmt |
format of the replacing string |
Returned values:
Returns a string with the made replacements.
Usage and examples:
DEFINE regex util.REGEX
DEFINE rs, rpl STRING
...
LET regex = /a|e|i|o|u/
CALL util.REGEX.replace(rs, regex, "[$&]")
...
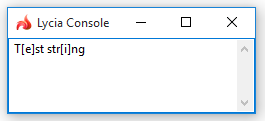
The examples above were taken from the example program.
Example programs:
CVS server: client.querix.com
CVS repository: /lycia_doc_examples
User: client
Project: library/regular_expressions
Related articles: