Top > Lycia reference > Querix 4GL > Regular expressions
Regular expression is a string which describes a pattern as a sequence of characters to be searched and found in a bigger character string (usually, a text).
In Querix 4gl, regular expressions can be used not only for text processing but also for more exact (as compared with the usual data type validation) validation of entered data.
Syntax:
/pattern/flags
Parameters:
|
pattern |
"text" of a regular expression, sequence of characters to be searched and found in a bigger character string |
|
flags |
modifiers added to specify additional search parameters (optional) |
Usage and examples:
![]()
Regular expressions are used to define search patterns for string matching.
To be able to search though long strings of characters, you need to:
→ create objects
util.REGEX - to hold the regular expression
util.MATCH_RESULTS - to hold the search results
DEFINE regex util.REGEX
DEFINE match util.MATCH_RESULTS
→ form a regular expression by combining alphanumeric and non-alphabetic (special) characters:
LET regex = /(\w+)\s(\w+)/
→ apply a regex algorithm:
LET r = util.REGEX.match("Test Libraries", regex)
CALL util.REGEX.search(res, regex) RETURNING match
LET rs = util.REGEX.replace("Test string", regex, "[$&]")
→ process the obtained results:
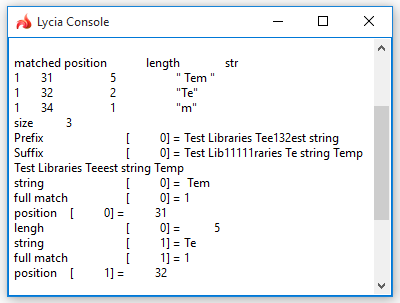
![]()
When used in regular expressions, control characters must be escaped to obtain the expected results:
\n - creates a newline symbol
\\n - searches for the "\n" expression and matches it to the regular expression in the sentence "\n is used to create a newline character".
Example programs:
CVS server: client.querix.com
CVS repository: /lycia_doc_examples
User: client
Project: library/regular_expressions