
qfgl is used to compile 4gl source files into intermediate representation modules (stored in .4o files).
Syntax:
qfgl [options] file_name.4gl
Possible options:
|
-? [ --usage ] |
displays usage information |
|
-V [ --version ] |
shows the version of the compiler |
|
-v [ --verbose ] |
produces verbose output (detailed compilation information) |
|
-d [ --database-driver ] arg |
sets database driver for compilation |
|
-e [ --encoding ] arg |
specifies the source file encoding |
|
-o [ --output ] arg |
determines the output path |
|
--java-option arg |
passes options to the Java Virtual Machine |
|
--check-help |
monitors all references to .erm help files (OPTIONS HELP FILE <path>) and checks whether help identifiers are present (HELP <id> for MENU) |
|
--check-kw |
switches on keyword warnings |
|
--no-warnings |
switches off all warnings |
|
-N [ --no-implicit-import-compile ] |
prevents implicit compilation of the file used in IMPORT FGL statement |
Usage and examples:
To compile a source code file a.4gl, invoke:
qfgl a.4gl
This will produce an IR module saved as a.4o to the output folder (by default, $LYCIA_DIR\bin).
If the following command is invoked:
qfgl –o b.4o –d sserver a.4gl
the output will be an IR module called b.4o, and the 4gl file will be validated against an SQL Server database.
-d is only used for validation purposes: The compiled program can be run against any database server available, either by using qfgl -d, or by setting the LYCIA_DB_DRIVER environment variable.
To compile files created with non-default encoding tables, -e must be followed by the specific value:
qfgl a.4gl -e Cp1252
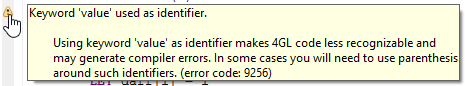
qfgl --check-kw switches on keyword warnings in LyciaStudio. This warning is displayed when a 4gl source file is build that includes variables which name coincide with a 4gl key word:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Keyword warnings can be also switched on and off in Building preferences.
Related articles:
Building Programs from Command Line