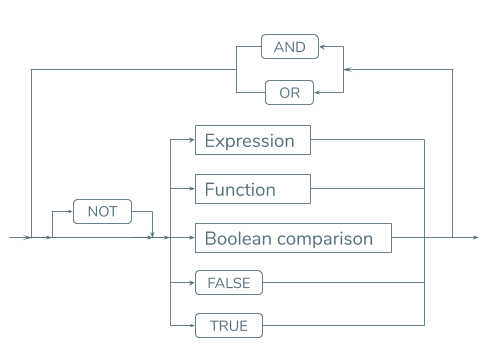
Boolean expressions
Boolean expression is a particular case of an integer expression that returns either TRUE of FALSE.
TRUE has the numeric value of 1, FALSE is equal to 0. In some cases, a Boolean expression can return NULL.
The syntax of a Boolean expression in a 4gl statement is not identical to the syntax of a Boolean expression in a SQL statement.
|
Expression |
a 4gl expression |
|
Boolean Comparison |
an expression that tests operands against the specified condition and returns a Boolean value |
|
Function |
a name of a function that returns a single value |
There are so called boolean operators and boolean comparisons that are used in the Boolean expressions.
Logical operators - AND, OR, NOT - combine one or more Boolean values into one Boolean expression.
Boolean comparisons are used to test the operands and to return boolean values.
|
Testing for |
Operators used in |
Example |
|
|
TRUE |
FALSE |
||
|
Equality or inequality of values |
Relational operators: == or =, <> or !=, <, >, <=, >= |
10<=100 |
"Tom" = "John" |
|
Equality or inequality of character strings |
MATCHES and LIKE |
IF "string" MATCHES "*rin*" |
IF "string" LIKE "%nir%" |
|
Null values |
IS NULL and IS NOT NULL |
IF text_var IS NOT NULL |
|
|
Correspondence of a value to a range |
BETWEEN … AND |
IF 5 BETWEEN 3 AND 12 |
IF 5 NOT BETWEEN 3 AND 12 |
|
Membership of a value |
IN() |
IF 4 NOT IN(1,2,3) |
IF 10 IN(6,7,8) |
Boolean expressions can belong to any other types of 4gl expressions.
For example, you can use INT and SMALLINT to store the value returned by a Boolean expression. However, if you compare two operands that have different data types, you might get unexpected results because numbers are usually compared with numbers, time values with time values, and character strings with character strings.
What Boolean expressions can return
Boolean expression can return TRUE, FALSE, or NULL based on the exact value they return and on the context in which this Boolean expression is used.
A Boolean expression is TRUE if it returns:
- a non-zero real number
- a character string that consists of a non-zero real number
- a non-zero INTERVAL value
- any DATE or DATETIME value
- a TRUE value returned by the INFIELD(field_name) operator if the cursor in is the field, field_name
- the built-in integer constant TRUE
A Boolean expression is also TRUE if it includes an operand with IS NULL and this operand returns TRUE.
A Boolean expression is NULL if it returns NULL and is not used in:
- a NULL test
- a Boolean comparison
- a 4gl conditional statement (WHILE, IF, or CASE)
In all the other cases a Boolean expression is evaluated as FALSE.
For example, if one or more elements of the Boolean comparison returns NULL, then all Boolean expressions used in a 4gl conditional statement are FALSE.