There are three basic ways to push your changes to the remote repository: use a Push wizard, push your changes to upstream, and commit and push them from the GIT Staging view.
![]() To be sure that your projects were properly pushed, confirm that all the GIT configurations were properly specified.
To be sure that your projects were properly pushed, confirm that all the GIT configurations were properly specified.
Push wizard is the most powerful way to push your changes to a remote repository.
|
Step 0 |
To be able to push your changes to a remote repository, you need its URL.
With Bitbucket, you can get the URL of your remote repository from Actions → Clone:
|
||||
|
Step 1 |
To start the Push wizard, right-click the selected project and go to Team → Remote → Push:
|
||||
|
Step 2 |
In the opened window, insert the URL of the remote repository you want to push to into the URI field:
|
||||
|
Step 3 |
The GIT plug-in will automatically retrieve the necessary information like the host, repository path, user, and password from the inserted URL (details can be found here):
|
||||
|
|
Once you have pushed to a repository, you'll be able to select it from the drop-down list (after pressing Ctrl+Space)or type the URL in directly :
Once you have configured Push from the GIT Repositories view, you will be able to select it from the drop-down list of Configured remote repositories:
|
||||
|
Step 4 |
After you press Next, you get to the Push Ref Specifications window where you configure your push:
Push Ref Specifications window is described below in more detail.
|
||||
|
Step 5 |
Once your push was configured, press Next to move to the Push confirmation window:
If you are sure about your commits, press Finish to start pushing:
|
||||
|
Step 6 |
Confirm your commit before it is pushed to the remote repository (you can return to the previous step if necessary):
For ref updates, you get the details of the pushed commits (as above); for refs which are deleted, you get [deleted]:
for refs which not exist yet, you get [new branch] or [new tag]:
for refs which contain now updates, you get [up to date]:
|
||||
|
Step 7 |
Before the push is complete, you'll get the Push results window where you will see what changes are pushed to the remote repository
|
||||
|
Step 8 |
Now all your changes were pushed to the remote repository:
|
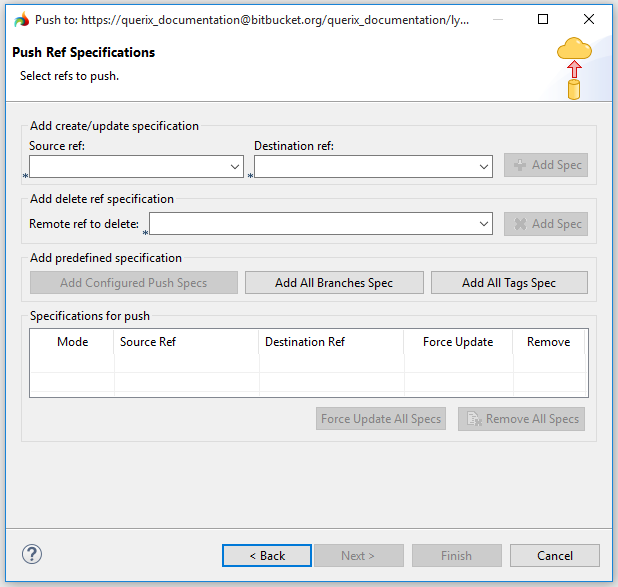
To push you changes to the remote repository, you have to define how your local branches and tags refer to remote ones (= specify references).
|
Add create/update specification |
specifies what local branch you want to map with what remote branch:
Source and destination branches are chosen among the existing ones from the drop-down lists:
Add Spec button sends the newly defined specification to the list of Specifications for push:
|
|
Add delete ref specification |
specifies what remote branch you want to delete: If you push Delete Ref Specification, the matching ref will be deleted from the destination folder:
The necessary specification can be selected from the drop-down list, or typed in directly (you may also use wildcards):
Add Spec button sends the newly defined specification to the list of Specifications for push:
|
|
Add predefined specification |
incorporates predefined specifications:
Add All Branches Spec declares that you want to map your local branch names to the same branch names on the repository you are pushing to. Add All Tags Spec declares that you want to map your local tags one-by-one to the same tags on the repository you are pushing to.
|
|
Specifications for push |
contains all the mappings to be pushed:
By default, in the case of a conflict you'll get the opportunity to solve it manually. If you check the Force update box for a specification
or press Force Update All Specs
you declare that in the case of the conflict new commits with overwrite the previous ones.
By pressing Remove All Specs
or clicking the dustbin icon
you'll remove the newly created specifications from the Specifications for push list (all of them or one by one):
|
If you add multiple Push Ref Specifications and they are in conflict, they will be colored in red. To solve such conflicts, you have to remove or edit the conflicting specs:

Once your have configured Push, you can commit you changes to the local repository and push them to the remote one simultaneously from the GIT Staging view:
|
Step 1 |
Perform the necessary actions at the Git Staging view and press Commit and Push:
|
|
Step 2 |
Wait until the procedure is over:
|
|
Step 3 |
Check Push results:
|
|
Step 4 |
Your changes were both committed to your local GIT repository:
and pushed to the remote one:
|
Typically, local branches fully correspond to the remote ones, and these remote branches contain all the information necessary to access the remote repository.
If so, you can configure Push in such a way that your local branches will be linked with the corresponding branches of the remote repository, and you will be able to push without specifying push refs (e.g. your local develop commits will be automatically pushed to your remote develop) - by pushing to upstream.
|
Step 1 |
To push to upstream, right-click the selected project and go to Team → Push to Upstream:
|
|
Step 2 |
Wait until the procedure is over:
|
|
Step 3 |
Check Push results:
|
|
Step 4 |
You changes were committed to the remote repository:
|
Both then Committing and Pushing and Pushing to upstream, you can configure Push by pressing Configure and going to the Push Configuration dialog:

Related articles:
Fetching from remote repositories
Pulling from remote repositories